While both Lean and Six Sigma aim to reduce waste, they are distinct methodologies. Six Sigma focuses on reducing defects by limiting variation within a process, while Lean removes unnecessary steps for a more efficient process. Combining these two methodologies can improve business performance by emphasizing both quality improvement and profitability. Learn more about Lean Six Sigma by reading Everything You Need to Know About Lean Six Sigma.
The acronym “DMAIC” represents a key aspect of Lean Six Sigma. DMAIC stands for the five phases of an improvement cycle: Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control. You can use these steps as a roadmap for resolving issues with a Six Sigma approach:
Define the project goals or problem to be addressed, internal and external customer requirements, and project boundaries.
Measure the current performance of the process and describe the process in quantifiable terms.
Analyze the process and identify the root causes of defects and sources of variation.
Improve performance by resolving the root causes of issues and eliminating defects.
Control future process performance by maintaining improvements.
Another version of this process is DMADV (Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, and Verify). The DMADV framework is typically applied to new products or services, rather than improving an existing process, or when an existing process has been improved but is not meeting a Six Sigma level. The process is similar to DMAIC but focuses on product or process design and how to implement that design effectively.
Six Sigma is a quality measurement that represents 3.4 Defects Per Million Opportunities. That’s a lofty goal for many business processes, but you can use Six Sigma methods to improve quality and performance in varying degrees based on the needs and objectives of a business or project. Six Sigma tools range from statistical charts, illustrative diagrams, and data collection methods to project management and process analyzation worksheets. These tools may not be exclusive to Six Sigma, but they can be applied in specific ways to focus on process improvement. The tools required depend on the project requirements and team roles. Depending on one’s training and experience, a Six Sigma professional may be involved in improvement initiatives at the White, Yellow, Green, or Black Belt level. White Belts generally have supporting roles, while Yellow Belts act as team members, Green Belts collect and analyze data, and Black Belts serve as project leaders.
In the following sections, you’ll find a number of free, downloadable templates that you can use as Six Sigma tools.
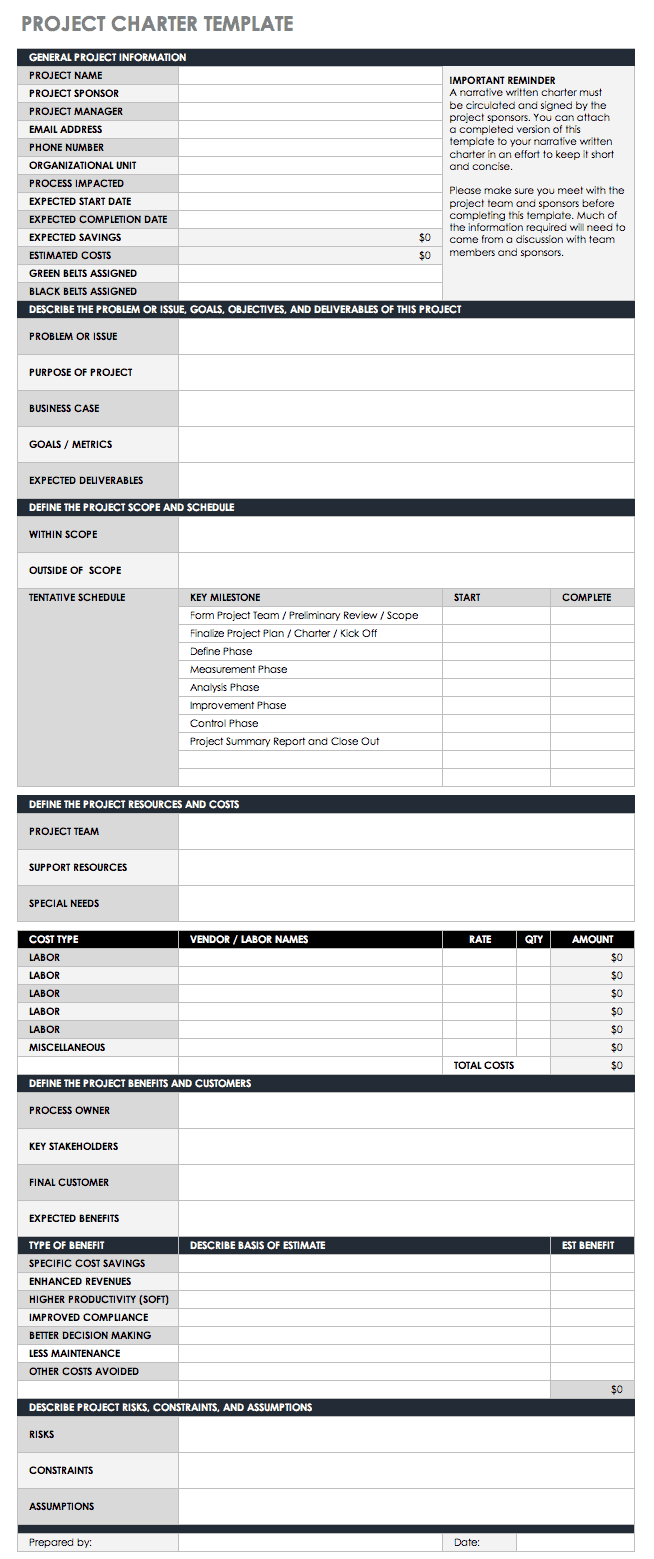
This Six Sigma Excel template is designed to help you create a project charter that will serve as an agreement between management and your team. A project charter provides an overview of a project including team roles and responsibilities, financial information, goals, and constraints. Creating a detailed project charter will help define your project and its expected outcome, and provide a high-level roadmap to follow.
It’s important to refer to previous research and planning to help create an effective action plan. Once you know what actions to take, this implementation plan template helps you organize them by priority, assign ownership, track progress, and update the plan as needed. This is an important Six Sigma tool for taking concrete actions toward achieving measurable objectives.
